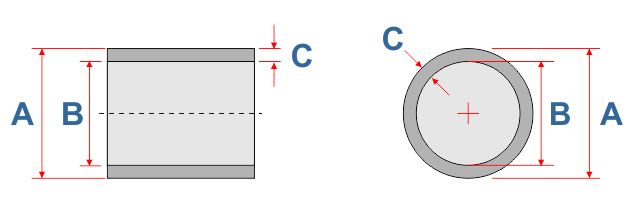
| NPS | OD (A) | ID (B) | Wall (C) | LB/FT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 4.8 | 0.148 | 4.486 | 0.95 |
| 6 | 6.9 | 0.212 | 6.451 | 1.96 |
| 8 | 9.05 | 0.278 | 8.461 | 3.37 |
| 10 | 11.1 | 0.342 | 10.375 | 5.08 |
| 12 | 13.2 | 0.406 | 12.339 | 7.18 |
| 14 | 15.3 | 0.471 | 14.301 | 9.65 |
| 16 | 17.4 | 0.536 | 16.264 | 12.49 |
| 18 | 19.5 | 0.6 | 18.228 | 15.67 |
| 20 | 21.6 | 0.665 | 20.19 | 19.24 |
| 24 | 25.8 | 0.794 | 24.117 | 27.44 |
| 30 | 32 | 0.985 | 29.912 | 42.22 |
| 36 | 38.3 | 1.179 | 35.801 | 60.43 |
| 42 | 44.5 | 1.37 | 41.596 | 81.59 |
| 48 | 50.8 | 1.563 | 47.486 | 106.34 |
Technical HDPE
The applications of High Density Poly Ethylene (HDPE) piping systems are varied; used for the Gas, Water, Drainage and Sewage Industries. HDPE is the most chemically inert of all commodity plastic raw materials and is therefore extremely chemical and corrosion resistant. Aggressive water resulting from high sulphate soils and low hardness water will not attack PE pipes. HDPE pipes are therefore resistant to a wide range of industrial waters and chemicals and offer an advantage in long-term systems life and manufacture costs.
Due to its non-metallic nature, the material used is totally resistant to all forms of metallic corrosion. Being made of a tasteless and odorless material, HDPE pipes remain neutral to all transported fluids. HDPE is completely inert and is widely used for transporting liquids made for human consumption. Because of their mirror – smooth inside surface, HDPE pipes have minimum flow head loss. There is also no buildup of inside deposits, a particular advantage in the construction of sewerage systems.
This gives HDPE pipes a significant long-term strength advantage over concrete and metal pipes. Polyethylene pipes have demonstrated, through testing and actual usage, that they meet and even exceed life service requirements for both pressure and drainage applications. A service life of 70+ years is projected where HDPE is specified. For years, engineers all over the world have specified HDPE pipes in chemically active acidic or alkaline site conditions.
